Phase Diagrams
Diagram
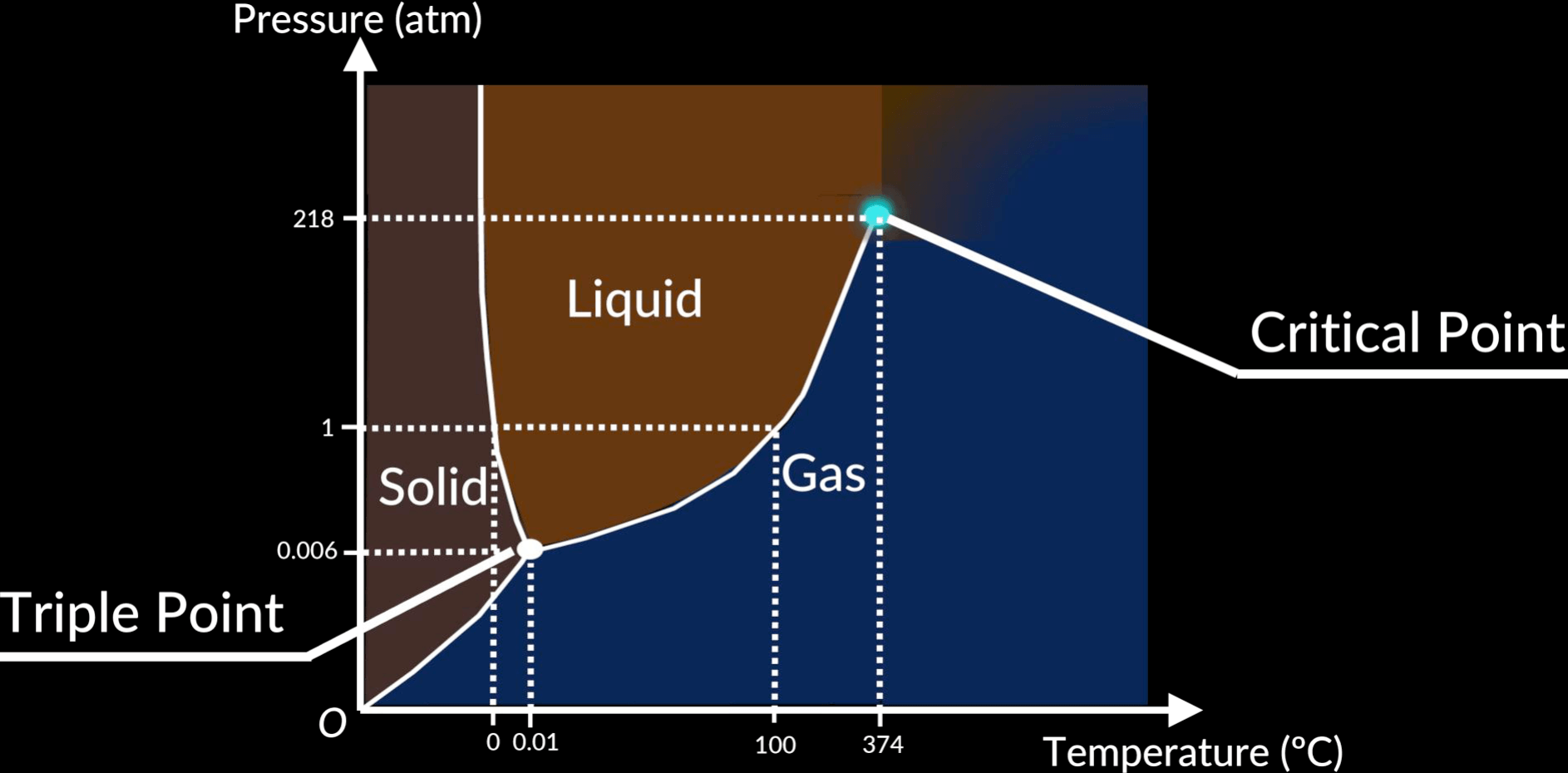
Info
- Triple point: the temperature and pressure at which all three phases of the substance can co-exist in thermodynamic equilibrium
- Normal boiling point: temperature at which the vapour pressure is equal to
- Critical point: from this temperature point forward, no matter what pressure we apply, we cannot liquify the gas
Example
Identify whether each of the following statements is true or false:
- A one-component phase diagram has a single triple point where solid, liquid and vapour phases co-exist.
- T
- A one-component phase diagram has a single critical point above which the liquid phase does not exist.
- T
- A liquid will boil (i.e. the vapour pressure above the liquid equals the total pressure) at a single temperature.
- F
- At a given pressure, above the triple point pressure, the solid phase melts at a single temperature.
- T
- At a given temperature (between the triple point and the critical temperature) vapour will begin to condense to liquid at a single pressure.
- T
Polymorphism
Definition
Polymorphism is the existence of a solid in more than one state
Phase Diagram for Water
Diagram
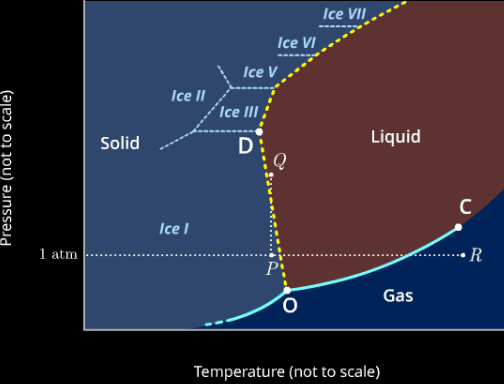
Observations:
- Multiple "triple points", but only one for all solid liquid gas
- Negative slope: melting point decreases with increasing pressure
Example
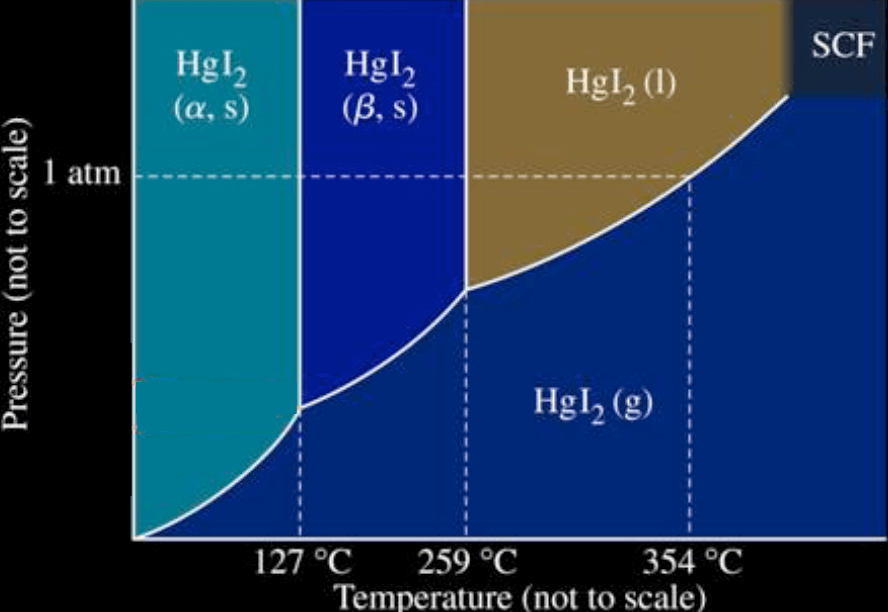
Identify whether each statement is A) TRUE or B) FALSE:
- There is a single triple point at which three phases are in equilibrium.
- F
- Mercury(II) iodide has a normal boiling point.
- T
- At temperatures below
, mercury(II) iodide does not melt. - T
- The vapour pressure of mercury(II) iodide at any given temperature could be determined from this phase diagram, if the axis were drawn to scale.
- T
- As pressure increases the sublimation temperature of mercury(II) iodide increases.
- T